Turning off your growbox for the summer? How to avoid it
Although Central Europe is not the Sahara, many indoor growers are forced to shut down their grow rooms during the hot summer months. Indoor-grown plants thrive best at room temperatures, and although they can withstand short periods of extreme heat, it will significantly affect their health and yield. In the end, it may not even be worth it for the grower to run the equipment. But how do you set up a grow room so you can really cultivate year-round?
Replace outdated discharge lamps with LED lighting
If you are still using discharge lamps (HPS, MH), summer is the ideal time to switch to LED grow lights. Discharge lamps emit a lot of heat and convert up to 70% of the consumed energy into infrared radiation, which directly heats the grow space and does not contribute to plant growth. LED fixtures have lower consumption and produce minimal heat, which will significantly reduce the temperature in the grow space. In addition, you will save on electricity bills, because compared to discharge lamps LED diodes convert much more of the supplied energy into photosynthetically active radiation in the PAR spectrum.
Pro tip: If you run lights during the day and struggle with high temperatures inside the grow space, try lighting the plants at night when it is cooler.
Improve ventilation and air circulation in the grow space
It is clear that the better and faster you can remove heated air from the grow space, the cooler it will be inside. But before you start buying new equipment, first check what you already have. A common cause of ventilation problems is clogged carbon filters and fans or leaking ducting and connections. If that does not help, try the following:
- Increase exhaust capacity: Check whether your fan can handle the increased load. Maybe it's time for a more powerful model.
- Maintain negative pressure in the grow box: Ideally, the exhaust performance should create a slight negative pressure in the grow tent. You can tell by the “sucked-in” walls of the grow box.
- Add circulation fans: Circulation fans not only help plants develop strong stems, but they also prevent hot air from accumulating in one place.
You might be interested in: Where and how to correctly place fans in a grow room
Air conditioning and cooling
If you have tried all the above tips and still need to lower the temperature in the grow box a bit, it’s time to reach for air conditioning. Air conditioning units are relatively expensive to run, so use them efficiently. Always exhaust the warm air from the air conditioning unit to the outside or to another room. Use timers and thermostats so the air conditioning runs only when absolutely necessary.
CO₂ supplementation
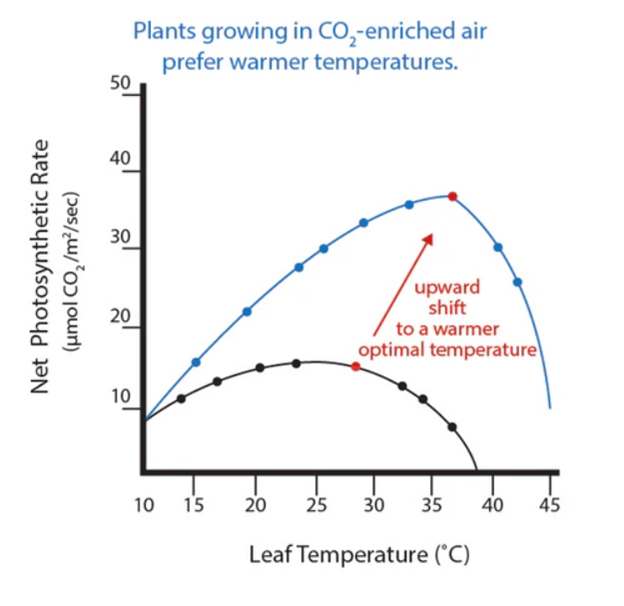
Although for most growers it is best to try to keep temperatures in the grow box within optimal values, under certain circumstances they can be advantageous. We are specifically talking about supplementing the atmosphere in the grow space with carbon dioxide. Plants use CO₂ during photosynthesis, during which they absorb light and convert it into energy in the form of glucose. Higher concentrations of carbon dioxide allow plants to carry out photosynthesis at higher temperatures. Under normal circumstances air contains about 400 ppm CO₂, which allows plants to photosynthesize efficiently at temperatures in the range of 25 to 30 °C. It has been found that if CO₂ content is increased to 1935, this temperature can rise to 36 °C.
Interested in the hot news from the growing field and practical tips for growers? Visit our Higarden blog.
